Mastoparan acetate(72093-21-1 free base)
CAS No. 79396-78-4
Mastoparan acetate(72093-21-1 free base)( —— )
Catalog No. M24793 CAS No. 79396-78-4
Mastoparan acetate is a peptide toxin from wasp venom.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 331 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 519 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 833 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1134 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1512 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMastoparan acetate(72093-21-1 free base)
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionMastoparan acetate is a peptide toxin from wasp venom.
-
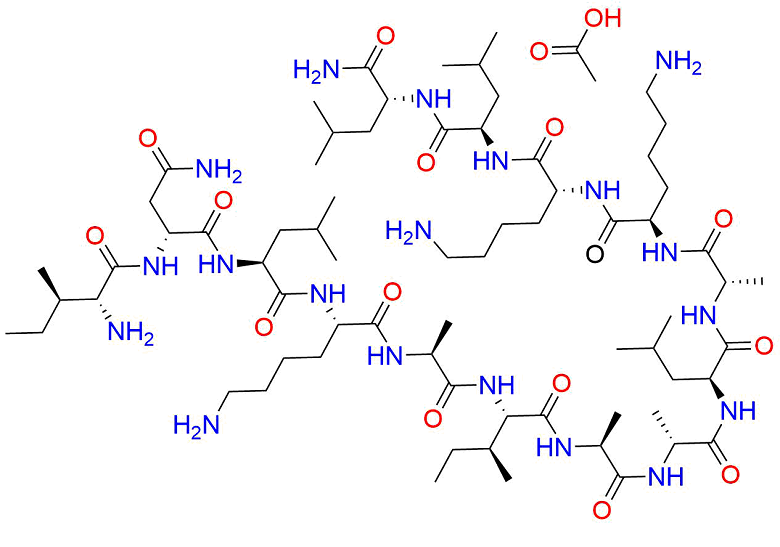
DescriptionMastoparan acetate is a peptide toxin from wasp venom. It has the chemical structure Ile-Asn-Leu-Lys-Ala-Leu-Ala-Ala-Leu-Ala-Lys-Lys-Ile-Leu-NH2.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number79396-78-4
-
Formula Weight1538.99
-
Molecular FormulaC72H135N19O17
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESO=C([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC([C@H]([C@H](CC)C)N)=O)CC(N)=O)=O)CC(C)C)=O)CCCCN)=O)C)=O)[C@H](CC)C)=O)C)=O)C)=O)CC(C)C)=O)C)=O)CCCCN)=O)CCCCN)N[C@H](C(N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(N)=O)=O)CC(C)C.CC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Mau SE, et al. Mastoparan, a wasp venom peptide, stimulates release of prolactin from cultured rat anterior pituitary cells. J Endocrinol. 1994 Jul;142(1):9-18.
molnova catalog



related products
-
W-2429
W-2429 (NSC294836) is a non-narcotic analgesic that may be used in the study of neurological disorders.
-
Iliparcil
Iliparcil is an antithrombotic compound with oral activity.
-
Sulfamonomethoxine
Sulfamonomethoxine is a long acting sulfonamide antibacterial agent.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


